Procurement
Procurement at H&Z is built on the conviction that sourcing is one of the most powerful value driver in any organisation. Our consulting approach combines strategy, digital enablement and operational excellence to strengthen performance across the entire supply base. We help organisations rethink how procurement works, enhance its impact and deliver sustainable value in an increasingly complex environment.

A FUNCTION WITH IMPACT
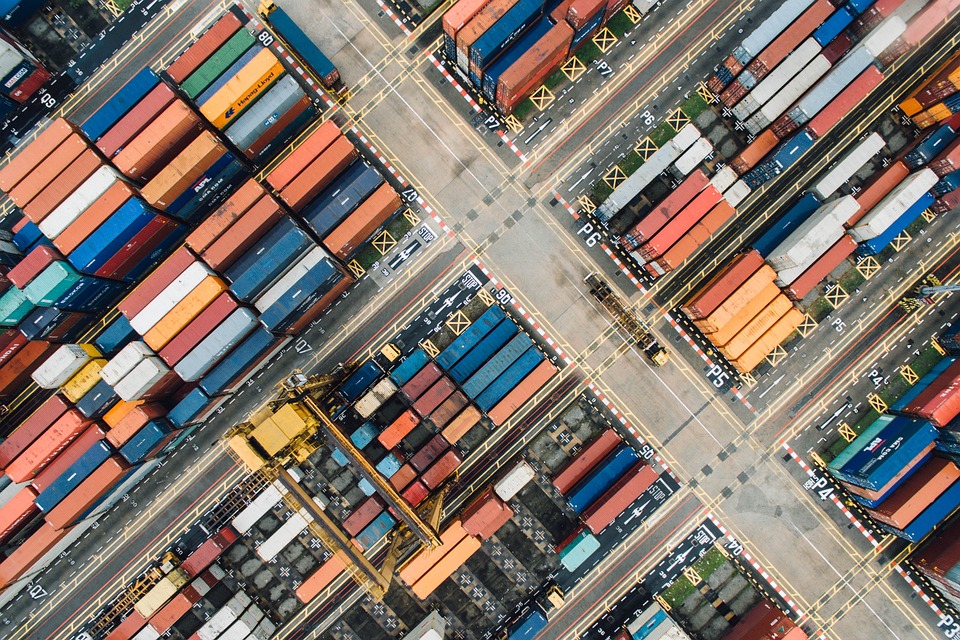
Procurement is Moving Beyond Cost
Procurement today plays a strategic role in managing risk, sustainability and resilience. Every company needs a procurement function that is agile, data-driven and aligned with business goals.
At H&Z, procurement consulting is part of our DNA. With more than twenty-five years of experience and over three thousand five hundred projects delivered, we help organisations turn procurement into a true value driver. Our work strengthens cost performance, builds resilient supply chains and supports long-term competitiveness.
We design procurement strategies that fit your business, combining industry experience with hands-on implementation to transform ambition into lasting impact.
Delivering Measurable Results
Our Procurement Service Offerings
Our Awards
How H&Z enables
B. Braun’s global procurement
Hear from our clients and experts on how procurement consulting creates tangible value and lasting capabilities. In this testimonial, B. Braun shares how H&Z supported their procurement transformation journey, combining digital enablement with category excellence.
SUCCESS STORIES
How We Help Procurement Leaders Succeed
Consulting With Head, Heart and Hand
Through this unique consulting approach, H&Z ensures sustainable results for international corporations and leading medium-sized companies.
Head
Our world is going to change more than ever before. We help our clients reinvent themselves and make a positive contribution to society.
Heart
We focus on proximity, create trust at all levels and give every individual the chance to participate. This is how success is achieved.
Hand
Our advisors are on site, listen and offer pragmatic solutions. We move forward with a clear course, generate courage for change and pave the way for top performance.
Our latest Insights
Implementation of Leading Procurement Platforms
Our implementation experts bring digital procurement strategies to life by deploying and integrating market-leading platforms such as Coupa, Ivalua and Jaggaer. With deep purchasing expertise and strong technical capability, we ensure that systems, data and interfaces work seamlessly across the organisation, enabling fast adoption and long-term digital performance.

The Procurement Initiative
We founded The Procurement Initiative, to bring together the leading procurement thinkers from business, academia and management consulting, to find fresh answers to the most significant challenges in procurement.

Let us help achieve your objectives
Our experts combine consulting excellence with deep industry experience to deliver procurement results that last.